The military organization is a structuring of the armed forces of a country so as to offer military capability. The military structure is totally hierarchical. In the past, to denote a particular position of a military hierarchy, the term ‘rank’ was used. The rank in the military organization symbolized the roles and responsibilities that the respective officer has to perform.
In the ancient military hierarchy, three terms were mainly used, such as rank, rate and grade. The army and the air force departments used the term rank in order to denote the respective position so their organizations. The naval or the coast guard organization used the term ‘rate’ in order to denote the respective positions. Grade is the term used for demonstrating the pay scales of the different military ranks.
In this particular editorial, we will describe in details about the ancient military hierarchy of the army, air force and he naval organizations. Here are some of the basic things to note first:
- During the ancient days, the basic unit of army was known as ‘Company’. The command of the company was in the hands of a commissioned officer on the rank of a captain.
- The commissioned officer who assisted the captain was known as the lieutenant. In case the lieutenant commanded a unit, it was called a platoon.
- The commissioned officers carried possessed a company flag known as the ensign. Under the commissioned officers, the positions were granted a warrant. These officers were called as warrant officers.
- The warrant officers were below the commissioned officers and above the non-commissioned officers in rank.
- The non-commissioned officers assisted the warrant officers and were given orders from them. The highest rank among the non-commissioned officers was called a sergeant. He commanded a squad.
- Below the sergeant were the corporals, who also commanded the squads and the veteran soldiers of the military organization.
So, basically in the ancient military hierarchy, there existed three levels of ranks. The top most rank was of the commissioned officers, the second being the warrant officers and the third rank being the noncommissioned officers.
Below are the general positions of the army that were prevalent in the ancient military hierarchy.
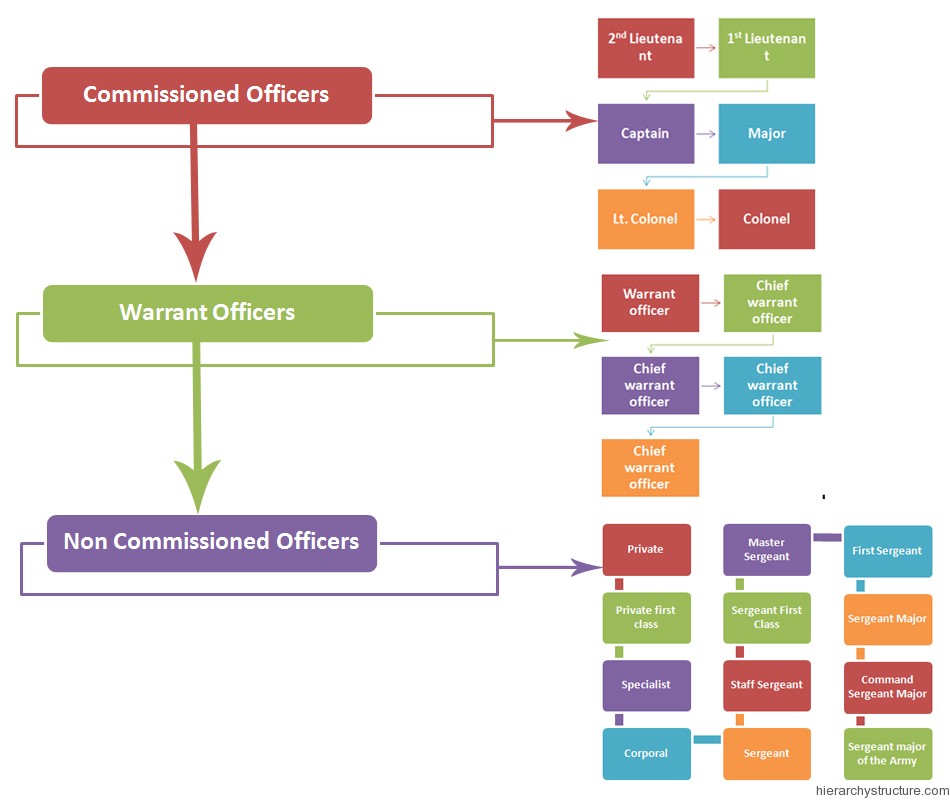
Commissioned Officers
- 2nd Lieutenant
- 1st Lieutenant
- Captain
- Major
- Lt. Colonel
- Colonel
Warrant Officers
- Warrant officer, one
- Chief warrant officer, two
- Chief warrant officer, three
- Chief warrant officer, four
- Chief warrant officer, five
Non Commissioned Officers
- Private
- Private first class
- Specialist
- Corporal
- Sergeant
- Staff Sergeant
- Sergeant First Class
- Master Sergeant
- First Sergeant
- Sergeant Major
- Command Sergeant Major
- Sergeant major of the Army.
In the naval organization, the ancient military hierarchy remained same for the commissioned officers and the warrant officers. The ranks for the non-commissioned officers were as follows:

- Seaman/Constructionman Recruit E-1
- Seaman/Constructionman E-2
- Seaman/Constructionman E-3
- Petty Officer Third Class
- Petty Officer Second Class
- Petty Officer First Class
- Chief Petty Officer
- Senior Chief Petty Officer
- Command Master Chief Petty Officer
- Master Chief Petty Officer
- Navy Guard
- Fleet Master Chief Petty Officer
Know more about Ancient Roman Military Hierarchy Click Here
