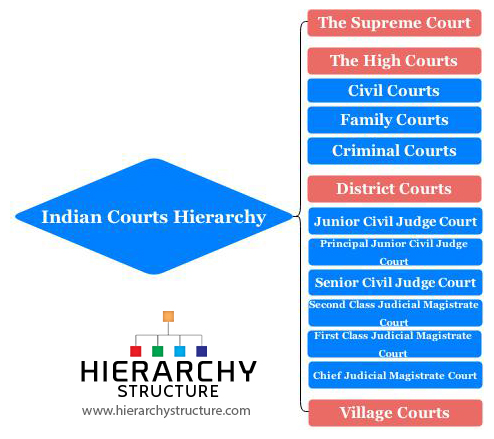
In India, there are various levels of judiciary which consist of different types of courts, each with a different set of powers and responsibilities. There is a strict hierarchy of importance among these courts which starts with the highest level court of the country and then moves down to less important courts in an even manner.
The Indian judiciary is independent of the legislative and executive branches of the government as defined by the Constitution. The Supreme Court is the highest level court, followed by the High court, district courts, village courts and many other court bodies. To understand this hierarchy of Indian courts better, you can go through the following given information.
 The Supreme Court
The Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of India is the apex court in the country, one which comprises of the Chief justice along with another 30 judges who are appointed by the President of India. The role of this court, as defined by the constitution is that of a federal court and it is the highest court of appeal. It is an appellate court which hears appeals against the decision of high courts.
The High Courts
There are a total of 24 High Courts in India, each functioning in the states of the country. These courts have jurisdiction over a state, a group of states or over a union territory. Below the High courts, come many different courts which handle various specific issues and cases of a certain nature. These are given as follows:
- Civil courts
- Family courts
- Criminal courts
District Courts
The district courts in India are established by the State governments in India and these are established in all the districts within states or union territories. Sometimes, a few districts are clubbed together and a court is given authority to handle their cases. These courts work under the administrative control of the High court of the state under which the district comes. The following are the subordinate courts which come under the district courts for each district:
- Junior civil judge court
- Principal junior civil judge court
- Senior civil judge court
- Second class judicial magistrate court
- First class judicial magistrate court
- Chief judicial magistrate court
Each of the district courts is headed by a District judge who is appointed by the State government.
Village Courts
Also known as Lok Adalats or Nyaya Panchayats, Village Courts are set up in villages to handle the appeals of the villagers on a wide range of matters.
Know more about Indian military Hierarchy: Click here
