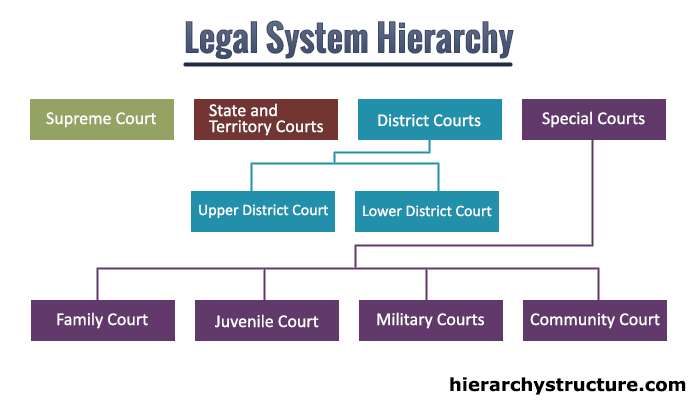
In Legal system hierarchy, a court is a chamber, often called a governmental institution which has the authority to settle legal disputes in between parties and also carry out the governance of justice in criminal, civil and administrative issues according to the system of the law. In both the common and civil law systems, courts are the vital mean for settlement of disputes. It is normally understood that every person has the ability to convey their issues before the court.
Likewise, the people who are charged for a crime have the right to defense before the court.In Legal system hierarchy, the court system which explicates and adhibits the law is together recognized as the judiciary. The Legal system court hierarchy is briefly elucidated as below in descending order means starting with the highest level court of the hierarchy and ending with the lowest one:
Supreme Court – In Legal system hierarchy, the Supreme Court is the uppermost of the court system. The Supreme Court hears appeals related to both the criminal and civil cases. Supreme Court also hears appeals that come from state and territory courts.
State and Territory Courts – In Legal system hierarchy, every state and territory has its own court. The authority related to every court differs from state to state and also from territory to territory.
District Courts – District Courts are the common trail courts of the legal court system. It deals with both the criminal and civil cases. It is the court of equity, admiralty and law. It has two level which are as follows:
- Upper District Court – The Upper District Court hears the issues concerning both civil and criminal cases. It also hears the appeal from the Lower District Courts.
- Lower District Court – It is the lowest among the court system. This court hears small issues related to civil and criminal cases.
Special Courts – There are some other special courts in the court system which are as follows:
- Family Court – The family court hears issues concerning family lawsuits. It also hears issues related to personal protection of husband or wife as well as violence against child. It hears issues related to divorce proceedings like custody of children, maintenance of wife and children, division of marital properties. It also hears cases related to adoptions.
- Juvenile Court – The Juvenile court deals with the offences of the persons who are below the age of 17. The Juvenile court is authorized with numerous options to deal with an offender who is a Juvenile. It also deals with the children who are beyond their parent’s control.
- Military Courts – Military courts are the courts for the appeal of the court martial. The court martial is conducted by the military personnel.
- Community Court – The Community Court deals with the cases such as, young offenders (aged 16 to 18), suicide attempted cases, offenders with mental disabilities, neighborhood disputes, carnal connection offences which are committed by young offenders, cruelty towards animals etc.