The political hierarchy of Japan is framed in an ardent and customized framework of a systematic parliamentary representative democratic monarchy. In Japan the Prime Minister is basically the head of the Cabinet as well as head of the government that directs the executive branch. In simple words the Japanese political hierarchy encompasses the multi party system and can be viewed as constitutional monarchy amid a system beneath civil law.
The Japanese political hierarchy is comprised of various levels like the Emperor, the legislative branch, the executive branch, the judiciary branch and many lower level bodies. These all covetous entities of the Japanese political system are described as follows starting with the highest rank and ending with the lowest one as described below in brief –
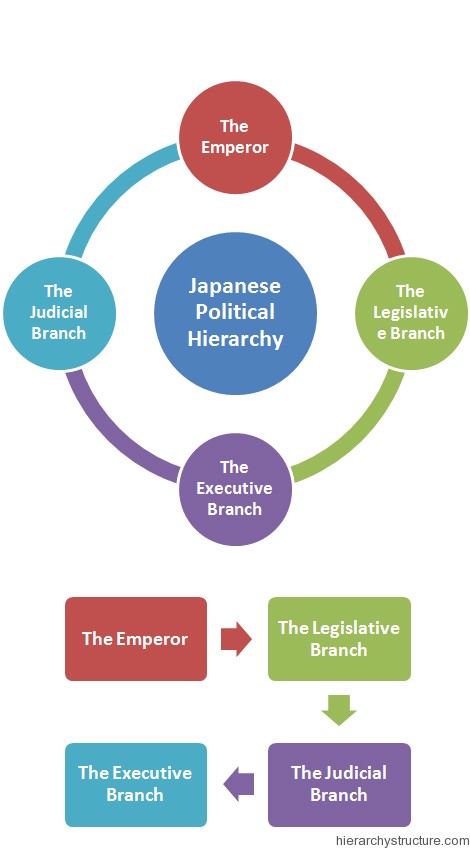
- The Emperor
- The Legislative Branch
- The Executive Branch
- The Judicial Branch
The Emperor
The Emperor is principally the ceremonial monarch in the Japanese political hierarchy and is also the head of the Imperial Japanese Family. The current Emperor who is reigning this honorable designation is honorable Mr. Akihito. The emperor possesses some special powers like appointment of prime minister as DIET’s designation, appointment of Chief Justice of the Supreme Court as per Cabinet’s designation. Further he possesses the power to promulgate government orders, laws, treaties and constitutions, along with the authority to convoke the Diet after consulting with the cabinet. Her even possess the power to dissolve the House of Representatives.
The Legislative Branch
The legislative branch incorporates three more branches aka the Diet, the House of Representatives and the House of the Councilors. The Diet is normally the most powerful from the three branches and further consists of above latter two branches. The Diet may direct to the Emperor in the appointment and removal of the chiefs of the executive and the judicial members. This branch is principally associated with formation of laws.
The Executive Branch
The executive branch is led by the Prime Minister, being head of the Cabinet. He is appointed by the Emperor but after being selected by the Diet members. He possesses the power to appoint as well as dismiss the Ministers of the state. Confidence of the House of the Representative is very much necessary for him to stay in the office. The current Prime Minister of Japan is honorable Mr. Shinzo Abe and was elected on 26th December, 2012.
The Judicial Branch
The judiciary system is an independent system in Japanese political hierarchy. The higher judicial members are appointed by the Emperor with the consensus of prime minister along with the cabinet members. In Japan, there are five court types that exist as per the law framework–Summary Court, Family Court, District Court, High Court and Supreme Court. But Only Supreme Court decisions have any direct effect on later interpretation of the law. In simple Japanese courts use a modified jury system and moreover there are no administrative courts or claim courts.
