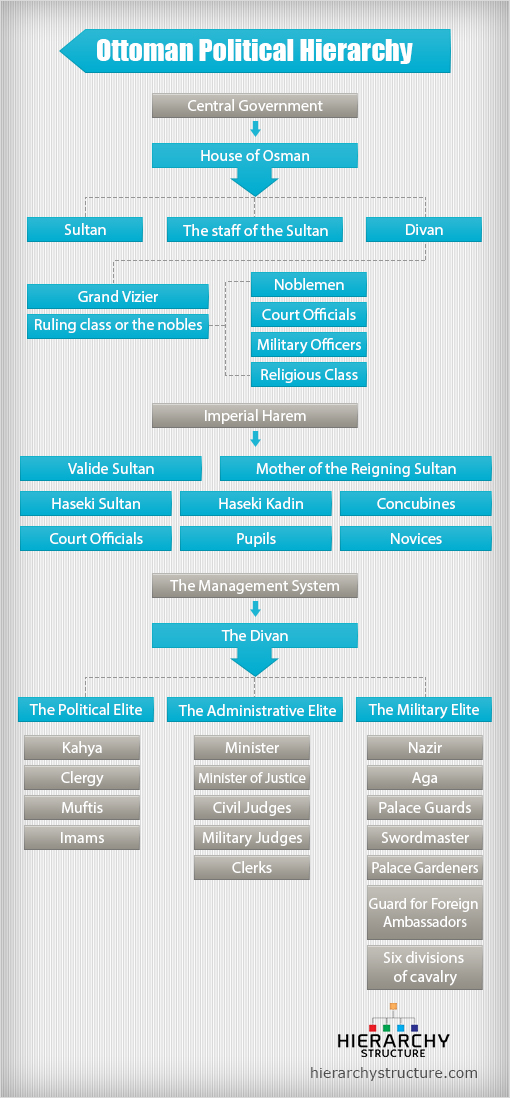
The Ottoman Empire ran for over many centuries and consisted of a complex governmental organization which has the Sultan at the top of the pyramid of the hierarchical structure. There was a systemic administrative organization in the empire which developed further into a dual system of civil administration and military administration. The entire hierarchical structure consisted of many positions, levels and areas of governance and rule. The following is a detailed structure given for your reference.
Central Government
The central government comprised of the Sultan at the top position and his staff. This was known as the House of Osman and this house was advised by the Divan. The Divan was also further subdivided and this is how the central government functioned. Here’s a proper structure:
House of Osman
- Sultan
- The staff of the Sultan including bookkeepers etc.
- Divan
- Grand Vizier
- Ruling class or the nobles
- Noblemen
- Court officials
- Military officers
- Religious class
Imperial Harem
As far as the Ottoman court was concerned, the Harem was the most important powers. The Harem had its own internal organization and a certain order for designing the policies. Here’s the hierarchical structure of the Imperial Harem
- Valide Sultan
- Mother of the reigning sultan
- Haseki sultan
- Haseki Kadin
- Concubines
- Court officials
- Pupils
- Novices
The Management System
The running and the management of the kingdom or province under the Sultan was done by the officials under him who were just and capable of handling the duties.
-
The Divan
The Divan was the council that advised the Sultan and the most powerful members of the Divan were the Viziers who were led by the Grand Divan.
The Political Elite
- Kahya
- Clergy
- Muftis
- Imams
The Administrative Elite
- Minister
- Minister of justice
- Civil judges
- Military court judges
- clerks
The Military Elite
- Nazir
- Aga
- Palace guards
- Swordmaster
- Palace gardeners
- Guard for foreign ambassadors
- Six divisions of cavalry
Provincial Government
Provincial government or civil government was responsible for ruling over the lower class which consisted of villagers, townspeople and farmers. There was a civil and judicial administration separately for the lower class. The lower class over which this system ran was called rayah both in modern usage and in contemporaneous usage as well.
- Kazas
- Qadi
- Nahiyas
- Millets
- Elders