The United States legal system hierarchy is well-known for having the most complicated and complex judicial systems in the whole world. Each day many people, including the officers of law enforcement, lawyers, government officials, judges and even charged criminals take part in this judicial system and hopes to resolve disputes and also work for the justice. This system is quite remarkable because of its ability to function successfully in the country as big and varied as the United States.
One of the reasons of this success is an impartial and very carefully ordered hierarchy. In United States legal system hierarchy, several kinds of federal courts control matters related to the federal law and every state has its individual set of courts that can adjust according to the needs of the people.
The United States legal system hierarchy is shortly elucidated as below in the chronological order which means starting with the highest level court of the hierarchy to the lowest level:
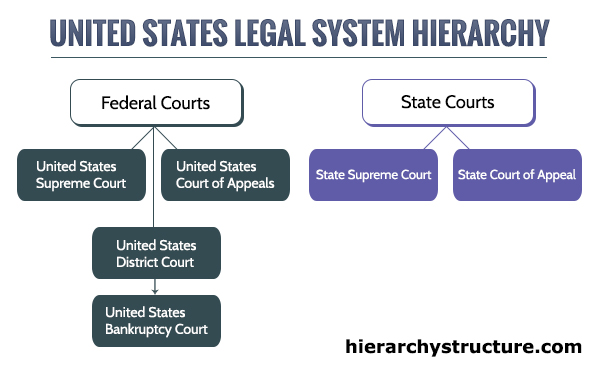
Federal Courts
In United States legal system hierarchy, the federal court system is formed by numerous levels of the hierarchical courts. It comprises of as follows:
- United States Supreme Court – Supreme Court is the uppermost federal court in United States. It has final authority to appeal over all the federal and state court cases which involves matters of federal law along with original authority over small cases. Supreme Court is the ultimate translator of the federal constitutional law.
- United States Court of Appeals – United States Court of Appeals are the intermediary appellate court of the federal court system. The court of appeals makes decisions on appeals which are from the district courts in its circuit of federal judiciary and in some cases from the other selected federal courts.
- United States District Court – Unites States District Courts are the common trail courts of the federal court system. It deals with both the criminal and civil cases. It is the court of equity, admiralty and law. The United States Bankruptcy Court is also connected with every United States District Court.
- United States Bankruptcy Court – These courts are formed under the Article 1 of the constitution of the United States. They work as units of district courts and have subject-matter authority over the cases of bankruptcy.
State Courts
In United States legal system hierarchy, there are wide variety of forms in State Courts as described by every state’s legislature. It comprises of as follows:
- State Supreme Court – The State Supreme Court is a trial level court of general authority in the court system of the state. In these courts counties with small populace share their justices.
- State Court of Appeal – The State Court of Appeals is the uppermost court in a particular state in the United States. It comprises seven judges of which one Chief Judge and six associate judges are assigned by Governor for the term of 14 years.